FAQs about LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging)
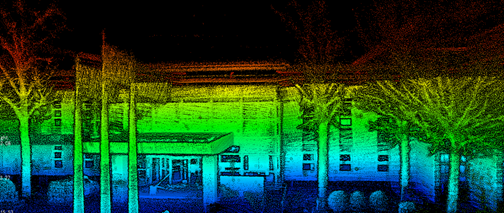
What is LiDAR?
LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technology that uses laser light to measure distances and create detailed 3D representations of objects and environments.
How does LiDAR work?
LiDAR works by emitting laser pulses and measuring the time it takes for the light to reflect off objects and return to the sensor. This data is used to calculate distances and create accurate 3D models.
What are the applications of LiDAR?
LiDAR is used in various applications including autonomous vehicles, forestry, agriculture, archaeology, urban planning, environmental monitoring, and more.
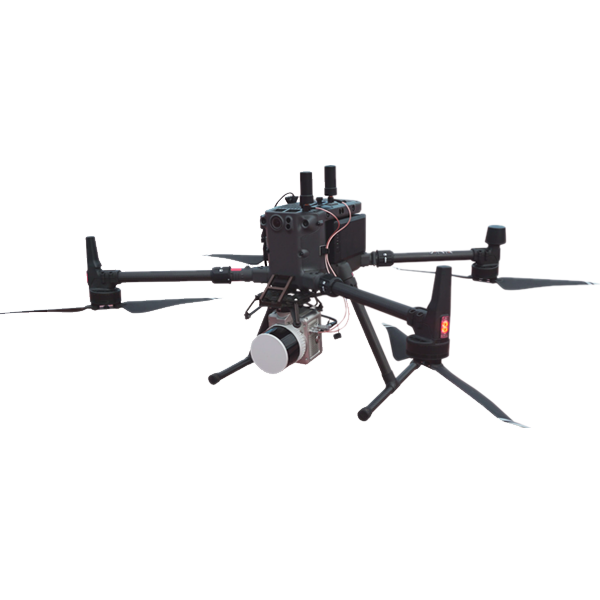
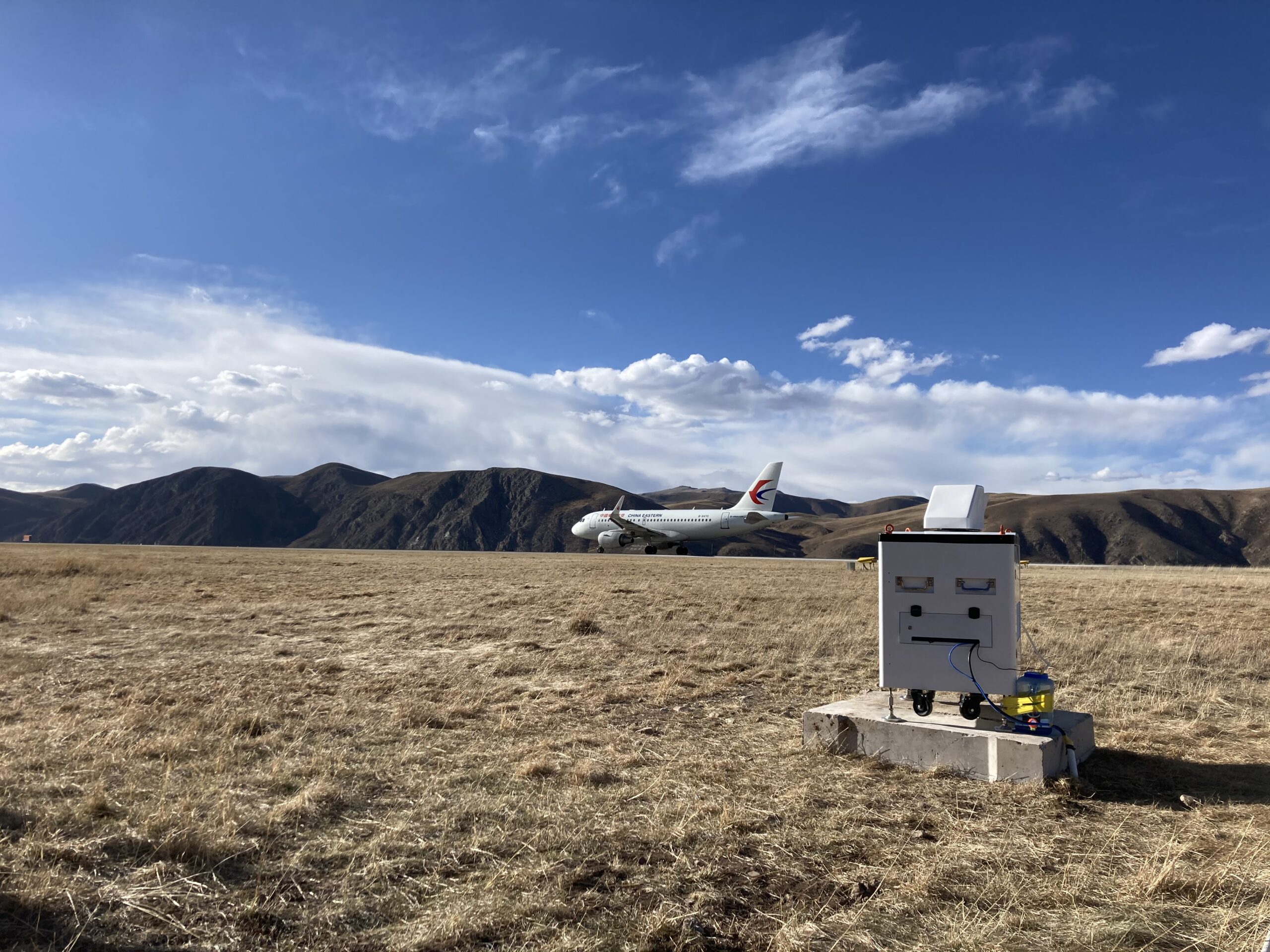


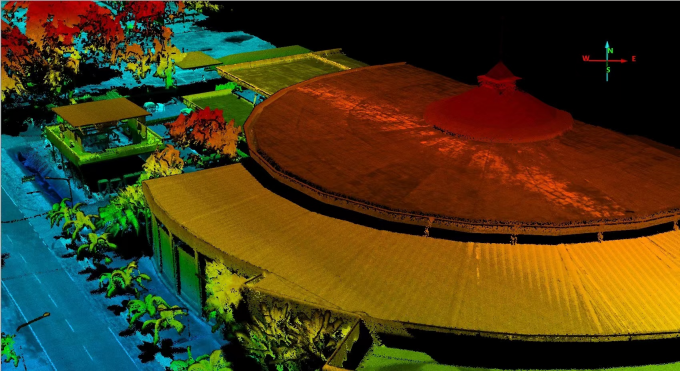
How is LiDAR used in autonomous vehicles?
LiDAR is a crucial sensor in autonomous vehicles, helping them create detailed maps of their surroundings and detect obstacles in real-time for safe navigation.
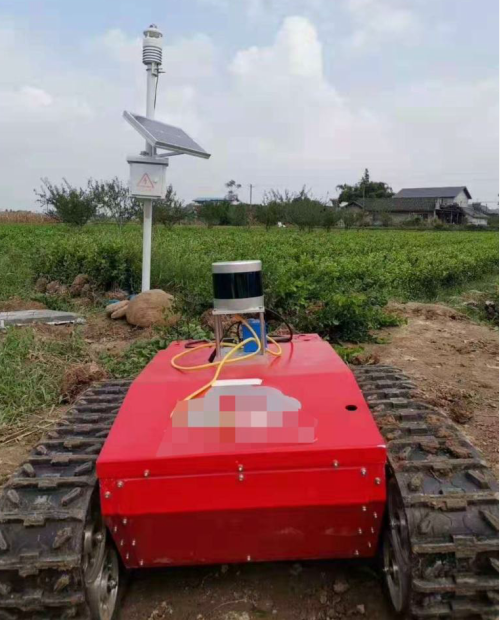
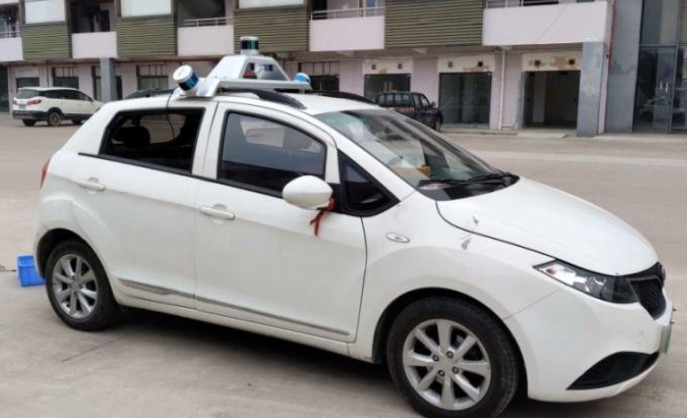



What are the types of LiDAR systems?
Survey LiDAR systems:
There are mainly two types of survey LiDAR systems: airborne LiDAR, which is mounted on aircraft for wide-area mapping, and terrestrial LiDAR, which is ground-based and captures detailed data of smaller areas.
Wind LiDAR systems:
Wind LiDAR uses doppler effect to measure the wind speed and direction, which can be applied for renewable, civil aviation and atomospheric monitoring. There are few types of them:
What's the difference between 2D and 3D LiDAR?
2D LiDAR only measures distances in a single plane, while 3D LiDAR measures distances in multiple directions, capturing a more comprehensive view of the environment. Here are the point cloud comparison between 2D & 3D LiDAR.
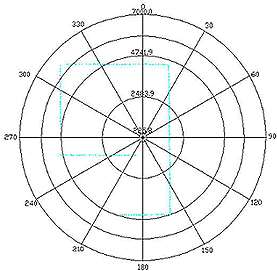
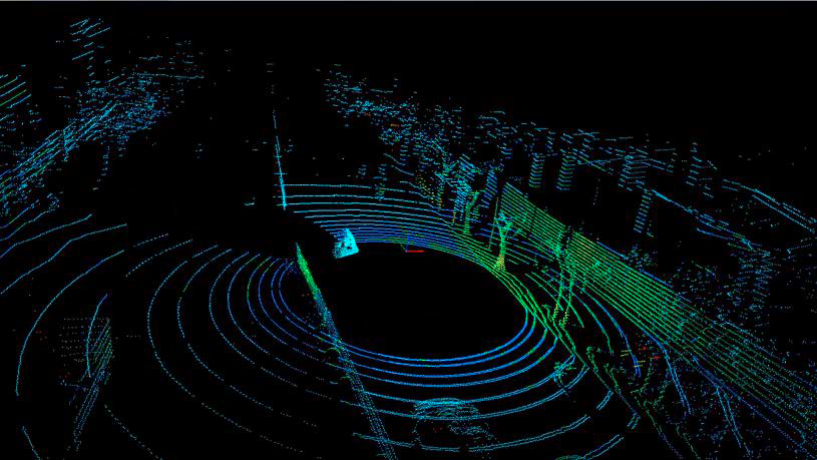
How accurate is LiDAR?
LiDAR can provide highly accurate distance measurements, often within a few centimeters. The accuracy depends on factors such as the type of LiDAR system, the quality of the equipment, and environmental conditions.
Most LiDARs use TOF (Time of Flight) measurement, the further the object is, the more accurate is the measurement, as it is more difficult to measure the time of the light travelling in the lower range.
What is the range of LiDAR?
The range of LiDAR can vary depending on the technology and equipment used. It can range from a few meters to several kilometers. Nowadays, most long range LiDARs use 1550nm wavelength light for detection.
How accurate is LiDAR?
LiDAR can provide highly accurate distance measurements, often within a few centimeters. The accuracy depends on factors such as the type of LiDAR system, the quality of the equipment, and environmental conditions.
Most LiDARs use TOF (Time of Flight) measurement, the further the object is, the more accurate is the measurement, as it is more difficult to measure the time of the light travelling in the lower range.
What's the difference between LiDAR and RADAR?
LiDAR uses laser light, while RADAR uses radio waves. LiDAR typically provides higher resolution and accuracy in detecting objects and capturing details.
Learn more about detailed comparison between LiDAR and RADAR.
Can LiDAR see through obstacles like walls?
No, LiDAR cannot see through solid obstacles like walls. It relies on the reflection of light, so if an object is obstructed from direct line of sight, LiDAR won’t be able to detect it.
Is LiDAR affected by weather conditions?
Yes, certain weather conditions like heavy rain, snow, or thick fog can affect LiDAR performance by scattering or absorbing the laser light.
How has LiDAR evolved over the years?
LiDAR technology has evolved to become more compact, affordable, and capable of higher accuracy and faster data collection. This has led to its integration in various industries.
What's the cost of LiDAR technology?
The cost of LiDAR systems can vary widely based on factors like the quality, range, and application. Costs have been decreasing over the years as technology advances.
Are there any privacy concerns related to LiDAR?
LiDAR can capture detailed information about environments and objects, raising potential privacy concerns in certain contexts, like surveillance or mapping of private properties.
However, LiDAR can only generate point cloud but not details like people face, so it is actually less violation to privacy than camera.
Can LiDAR work at night?
Yes, LiDAR can work at night since it emits its own light source (laser). This makes it useful for applications where visibility is limited in low-light conditions.
How does LiDAR contribute to environmental conservation?
LiDAR is used in forestry to measure tree height, density, and structure. It also helps in monitoring deforestation, wildlife habitats, and ecosystem changes.
Can LiDAR be used for underwater mapping?
Yes, LiDAR can be used for underwater mapping by using specially designed systems. It’s used for marine research, coastal management, and underwater archaeology.
What's the role of LiDAR in disaster management?
LiDAR can assist in disaster management by providing rapid and accurate 3D maps of disaster-affected areas, helping responders plan and execute rescue operations more effectively.
How does LiDAR help in archaeological research?
Archaeologists use LiDAR to map ancient landscapes, locate buried structures, and uncover archaeological sites that might be hidden by vegetation or other obstructions.
What's the future of LiDAR technology?
The future of LiDAR holds potential for even more miniaturisation, improved performance, integration with AI for better object recognition, and wider adoption in industries beyond its current applications.
How is LiDAR employed for gas mapping?
LiDAR is used for gas mapping by emitting laser pulses that interact with gases in the atmosphere, including trace amounts of specific gases like methane. By analysing the way these laser pulses are absorbed and reflected, LiDAR can create maps of gas concentrations, aiding in the identification and monitoring of gas emissions.
How do active and passive remote sensors differ in their functions?
Active remote sensors, like LiDAR, emit their own energy (such as laser light) and measure the reflected signal. Passive remote sensors, like cameras or thermal sensors, detect natural energy (like sunlight or heat) emitted or reflected by objects. Active sensors provide more control over data acquisition, while passive sensors rely on external energy sources.
Within the oil and gas supply chain, what segments can gas mapping LiDAR survey?
Gas mapping LiDAR can survey various segments of the oil and gas supply chain, including production facilities, pipelines, storage tanks, and distribution infrastructure. It provides insights into methane emissions and leak detection, contributing to more efficient and environmentally responsible operations.
